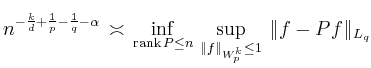
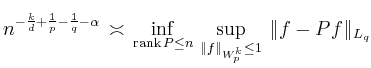
Asymptotically optimal approximation operators ![]() improve the exponent for standard schemes,
such as spline interpolants or finite element
projections, by
improve the exponent for standard schemes,
such as spline interpolants or finite element
projections, by ![]() .
The gain is maximal for
.
The gain is maximal for ![]() ,
, ![]() , when
, when
![]() .
.
![\includegraphics[width=10cm]{ApproximationFig.eps}](img18.png)
The figure shows the exponents for all values of
![]() .
Apparently, classical methods are optimal for
.
Apparently, classical methods are optimal for ![]() and
and
![]() (white area).
(white area).
![]() Dissertation, Bonn, 1979
Dissertation, Bonn, 1979
![]() Math. Annalen, 242 (1979), 273-281
Math. Annalen, 242 (1979), 273-281
| [previous] | [next] |